Current media focus is directed towards the issue of rising energy and living costs. Rinnai continuously works to produce robust and reliable products that benefit the customer in terms of finance and performance.
Rinnai’s instantaneous hot water systems have been rigorously analysed and found to offer significant savings in five key areas, when compared to traditional storage systems: running costs, initial payments, carbon footprint, space and weight.
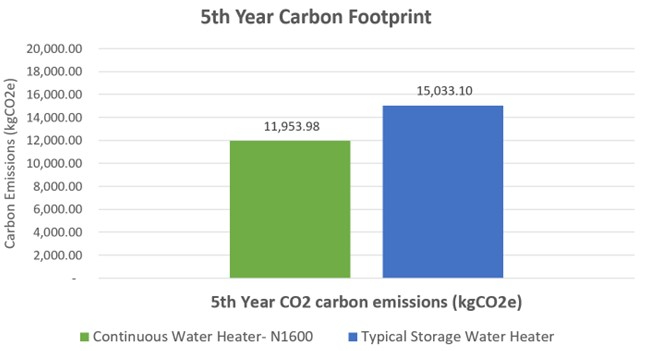
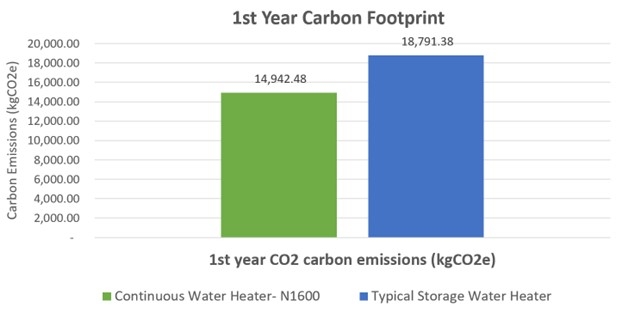
Below features two graphs that visually demonstrate levels of emissions released by both a storage hot water system and a Rinnai N1600. The first graph reveals 1st year carbon footprint; the second establishes the difference after a period of 5 years.
The blue right-side column represents the total emissions released by a typical water storage system which is measured at nearly 19,000 kg of carbon dioxide. Rinnai’s N1600 is responsible for UNDER 15,000 kg of carbon dioxide.
The below graph provides visual information that proves over 5 years, Rinnai’s N1600 continuous flow hot water heater release less emissions than a traditional storage water heater when measuring kg’s of carbon dioxide.